00:00:15.379
Hello everyone! I think that Ruby is one of the most amazing programming communities, and today we will explore the fun of hijacking Ruby syntax.
00:00:27.750
We will discuss how to hijack Ruby syntax and showcase the power of Ruby metaprogramming.
00:00:39.260
First, let me introduce myself: my name is Tomohiro Hashidate, and I come from Japan. My friends call me Joker, due to my personality.
00:00:55.649
I work as a data engineer and have experience in web application engineering, which has made me quite familiar with Ruby and Ruby on Rails.
00:01:10.290
This is my first trip to the United States, and it is also my first time giving a talk like this. I am a bit nervous, but I am very happy to be here.
00:01:30.869
Next, I'd like to introduce my partner, Satoshi Tagomori, who will be joining me. I am an open-source software developer and manage several projects, including Groovy and others.
00:01:54.149
I'm currently working at a tech company as a software developer in the IoT services division, providing enterprise data analytics platforms.
00:02:18.490
Satoshi and I work at different companies, but we come together through the great Ruby community in Tokyo, where we discuss interesting programming techniques.
00:02:31.470
In this talk, we will introduce some Ruby features and share our own code that utilizes these metaprogramming techniques.
00:02:47.620
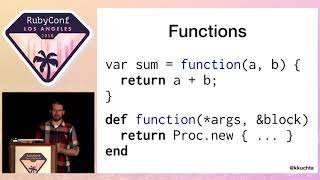
First, I want to talk about 'Binding.' Binding is a context object that includes local variables and instance variables. It is often used in template engines.
00:03:05.660
This sample code shows how to retrieve a binding object from context or method, using 'get_binding' to access the values of local variables and instance variables.
00:03:32.229
Notably, binding allows us to access values like local variable 'n' or instance variable 'secret,' demonstrating its flexibility.
00:03:50.770
The code shows how to obtain a binding object through the 'binding-proxy' method, enabling us to access variables defined as 'a', 'b', and 'c'.
00:04:16.950
Though this binding object can be utilized to set new local variables, it's important to note that these new variables only exist in the context of that binding.
00:04:40.750
For example, setting 'D' in one context does not allow it to persist in another. This behavior of Binding allows for flexible yet controlled variable management.
00:05:06.190
Next, let's explore 'TracePoint.' This Ruby feature allows the tracing of events within the Ruby Virtual Machine and enables hooks for various events.
00:05:32.970
We can hook into many events, such as method calls, class definition beginnings, and method returns. It allows us to gather information for various purposes, including exception handling.
00:05:52.900
The sample code demonstrates a simple method definition that takes an argument and returns a string, showcasing how TracePoint can interact with local variables.
00:06:24.090
Interestingly, when TracePoint is enabled, the behavior of method calls can change based on the method's context, allowing us to manipulate and observe variable states.
00:06:47.970
Next, I will talk about refinements, a method of extending classes locally to improve safety. Most Rubyists are not fully aware of this feature.
00:07:28.470
Refinements can create super-private methods, allowing our defined methods to be used within this file only, aiding in refactoring and controlling visibility.
00:08:07.800
I also want to talk about method hooks, which are not very popular but can provide a lot of potential for Ruby methods.
00:08:39.020
These hooks allow us to track method definitions and provide ways to implement method modifiers like 'final', 'override', and others.
00:09:12.800
These method modifiers also suggest similarities to methods in Java, which might make them easier to understand for users transitioning from Java.
00:09:50.380
By using these techniques, we can redefine behaviors in Ruby, effectively allowing modifications similar to what can be achieved through hooks.
00:10:33.480
However, caution must be exercised; misusing or forgetting to disable hooks can result in unintended consequences, making debugging more difficult.
00:11:06.240
For instance, combining these techniques with threading and execution flow may introduce complex bugs that are hard to trace.
00:11:26.220
It's essential to understand when to leverage binding and TracePoint to control which variables are accessed, manipulated, and released during execution.
00:12:02.560
As we continue with our presentation, we aim to illustrate how utilizing these advanced features can enhance Ruby applications, from memory management to robust error handling.
00:12:50.510
Finally, we'll discuss safe resource allocation, referencing the existing syntax of languages like Java, which readily provides resource management techniques.
00:13:57.840
In Ruby, we can achieve this through a simplified syntax, utilizing features like 'with' in conjunction with top-level scope definitions to manage resources intelligently.
00:15:10.690
The implementation allows for block-level resource assignment, ensuring that resources can be allocated and deallocated seamlessly, promoting better memory management.
00:15:50.560
Furthermore, the adjustments made around resource handling not only streamline operations but also facilitate cleaner, more readable code structures.
00:16:21.440
This transition to more advanced resource management structures aligns with our ongoing efforts to make Ruby an even more powerful and efficient programming language.
00:16:56.240
As we wrap up our talk, we hope to leave you with a better understanding of how to utilize these metaprogramming techniques creatively and effectively in your Ruby projects.
00:18:00.680
Thank you for your time, and we are happy to take any questions you might have as we embark on this exciting journey through Ruby.